- ligand
-
ligand [ ligɑ̃ ] n. m.• 1959; mot angl., du lat. ligandum, gérond. de ligare « lier »♦ Chim. Molécule, ion uni à l'atome central d'un complexe par une liaison de coordinence.♢ Biochim. Petite molécule se fixant à une protéine par des liaisons spécifiques et non covalentes.
● ligand nom masculin (anglais ligand, du latin ligare, lier) Molécule ou ion unis à l'atome central d'un complexe par une liaison de coordination.⇒LIGAND, subst. masc.BIOCHIM. Molécule caractérisée par sa tendance à se lier à une autre (LEND.-DELAV. Biol. 1979). On donne le nom de « ligand » à un corps caractérisé comme tendant à se lier à un autre (J. MONOD, Le Hasard et la Nécessité, 1970, p. 93 ds REY-GAGNON Anglic. 1980).— P. méton. Groupement ainsi coordonné. En tenant compte de leur conductibilité et de diverses autres propriétés, il aboutit à la conclusion que, dans ces molécules, l'ion du métal principal (centre coordinateur) est entouré par un nombre constant et caractéristique de molécules, et d'ions (plus tard nommés groupements ou « ligands ») (Hist. gén. sc., t. 3, vol. 2, 1964, p. 421).Prononc. : [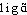 ]. Étymol. et Hist. 1959 (DUVAL). Terme formé, en angl. (1952 ds NED Suppl.2), sur le gérondif du lat. ligare « lier ».ligand [ligɑ̃] n. m.ÉTYM. 1959, in T. L. F.; mot angl. des États-Unis (1952), du lat. ligandum, gérondif de ligare « lier » (→ Lier).❖♦ Chim. (Anglic.). Molécule, ion dans lesquels un atome central est lié à d'autres atomes ou groupements d'atomes en nombre supérieur à la charge ou au degré d'oxydation de l'atome central. — Équivalent proposé : coordinat.1 On donne le nom de « ligand » à un corps caractérisé comme tendant à se lier à un autre.Jacques Monod, le Hasard et la Nécessité, p. 93 (note).2 (…) les propriétés de reconnaissance stéréospécifiques de la protéine sont modifiées par la transition. Par exemple dans l'état « R », la protéine pourra s'associer à un ligand α, mais non à un autre ligand β qui, lui, sera reconnu (à l'exclusion d'α) par l'état « T ». La présence d'un des ligands aura donc pour effet de stabiliser l'un des états aux dépens de l'autre, et l'on voit qu'α et β seront antagonistes l'un de l'autre, puisque leurs associations respectives avec la protéine sont mutuellement exclusives. Supposons maintenant un troisième ligand γ (qui pourrait être le substrat) s'associant exclusivement avec la forme R, en une région de la molécule autre que celle où se fixe α. On voit que α et γ coopéreront à la stabilisation de la protéine dans l'état actif (celui qui reconnaît le substrat). Le ligand α et le substrat γ agiront donc comme activateurs, le ligand β comme inhibiteur.Jacques Monod, le Hasard et la Nécessité, p. 94.❖HOM. Forme du v. liguer.
]. Étymol. et Hist. 1959 (DUVAL). Terme formé, en angl. (1952 ds NED Suppl.2), sur le gérondif du lat. ligare « lier ».ligand [ligɑ̃] n. m.ÉTYM. 1959, in T. L. F.; mot angl. des États-Unis (1952), du lat. ligandum, gérondif de ligare « lier » (→ Lier).❖♦ Chim. (Anglic.). Molécule, ion dans lesquels un atome central est lié à d'autres atomes ou groupements d'atomes en nombre supérieur à la charge ou au degré d'oxydation de l'atome central. — Équivalent proposé : coordinat.1 On donne le nom de « ligand » à un corps caractérisé comme tendant à se lier à un autre.Jacques Monod, le Hasard et la Nécessité, p. 93 (note).2 (…) les propriétés de reconnaissance stéréospécifiques de la protéine sont modifiées par la transition. Par exemple dans l'état « R », la protéine pourra s'associer à un ligand α, mais non à un autre ligand β qui, lui, sera reconnu (à l'exclusion d'α) par l'état « T ». La présence d'un des ligands aura donc pour effet de stabiliser l'un des états aux dépens de l'autre, et l'on voit qu'α et β seront antagonistes l'un de l'autre, puisque leurs associations respectives avec la protéine sont mutuellement exclusives. Supposons maintenant un troisième ligand γ (qui pourrait être le substrat) s'associant exclusivement avec la forme R, en une région de la molécule autre que celle où se fixe α. On voit que α et γ coopéreront à la stabilisation de la protéine dans l'état actif (celui qui reconnaît le substrat). Le ligand α et le substrat γ agiront donc comme activateurs, le ligand β comme inhibiteur.Jacques Monod, le Hasard et la Nécessité, p. 94.❖HOM. Forme du v. liguer.
Encyclopédie Universelle. 2012.
